Treatment of prostatitis in men: signs and symptoms
Treatment of Prostatitis in Men: Signs and Symptoms
What is the prostate in men, and why is it needed? This organ provides sperm motility, as its cells produce a special secret that gives sperm a liquid consistency. In the tissue of the prostate gland, hormones responsible for men's health are synthesized. They control the metabolism of proteins and carbohydrates in the body of a man, maintain the tone of smooth muscle cells of the body (including the prostate gland itself), and cause a normal erection. Therefore, in the case of the disease, treatment of prostatitis and its symptoms is required.
Why do I need a prostate?
The anatomy of the prostate gland is designed in such a way that it takes part in the process of urine excretion, controlling urination with the help of the muscular sphincter. He is responsible for the release of seminal fluid at the time of ejaculation.
Any violation of the functional activity of the male prostate leads to a malfunction not only in the genitourinary system, but also in the entire body: the heart and blood vessels are disturbed, there are problems with erection, sleep, a change in metabolism, irritability, apathy, depression, fatigue and others disorders of the nervous system. Therefore, if symptoms of male prostatitis appear, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. You can also use a special device - a prostate massager Prostata help MP-1
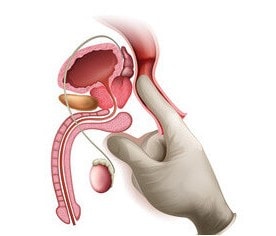
The anatomical structure of the prostate
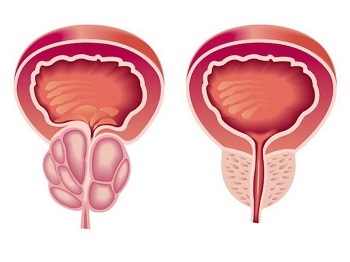
To get rid of prostatitis at home, you need to know the anatomy well. The above functions are facilitated by the structure or anatomy of the prostate gland. The prostate is located under the bladder so that the urethra passes through it, dividing into two halves (the prostatic part of the urethra in the structure of the prostate gland). The seminal ducts are also located here. The mass, size and volume of an organ depend on age, constitution, hormonal levels, concomitant diseases and other factors. Externally, the organ is trapezoid or chestnut-shaped. The tissue composition of the organ is represented by smooth muscle, connective tissue, glandular and lymphoid cells.
Types of Prostatitis
Each type of prostatitis has its own varieties, and the right choice of medication for prostatitis depends on the particular type. In general, inflammation of the prostate can be infectious or non-infectious. In the first case, the disease develops as a result of penetration into the organ of infection. The medicine for prostatitis. Depending on its type, the following types of disease are distinguished:
fungal;
Infectious agents can enter the prostate in many ways. For example, if the infection got into the gland tissue from the lower parts of the urethra, then such prostatitis is called ascending, and if from the upper urinary organs, then descending. In addition, such types of prostatitis are distinguished as:
lymphogenous (infection penetrates with lymphatic flow);
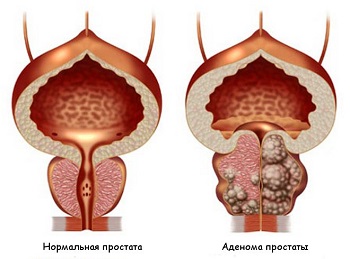
Another type of inflammation of the prostate in men - non-infectious - also has its own classification of subtypes. So, it can be calculous, in which stones form as a result of the penetration of urine into the ducts of the prostate. Age-related prostatitis - develops around 35-40 years; symptoms may be absent. The third subspecies of non-infectious prostatitis in men is stagnant. It occurs, as a rule, as a result of a sedentary lifestyle and insufficient sexual activity.
In addition to these varieties, prostatitis can be acute and chronic. The first begins suddenly, abruptly, proceeds with severe pain, radiating to neighboring parts of the body in different directions. In the chronic course of the disease, its symptoms may be mild or absent.
Causes of prostatitis in men
Every man should know what causes prostatitis. Prostatitis symptoms and treatment depend on the cause. This will help both to avoid or prevent prostatitis, and to choose the right therapeutic direction. The causes of prostatitis in men are divided into those associated with the infection and independent of it. The first group of factors includes:
the course of infectious processes in the body (urinary tract infections, sinusitis, and others);
STDs
penetration of infection during surgery and the like.
Among the non-infectious causes of prostatitis in men, there are:
weak immunity;
lack of physical activity;
bad habits (drinking);
lack of sexual activity for a long time;
increased sexual activity;
hormonal imbalance;
hypothermia and others.
In addition, the prostate becomes inflamed due to impaired blood flow (lack of nutrients and oxygen), disorders of the lymphatic system both in the gland and in the structures surrounding it. Another cause of prostate inflammation in men is a violation of the functional activity of the endocrine system. Hormonal failure leads to androgen deficiency.
Whatever the cause of prostatitis, only a doctor can prescribe a treatment for the disease based on diagnostic data and clinical symptoms.
Signs and Symptoms
For effective treatment of inflammation of the prostate gland, it is important to notice the first signs of prostatitis in time, which depend on the form of pathology, then you can understand how to treat prostatitis. In many men, the acute form of the disease begins with the appearance of unpleasant or painful sensations in the groin, perineum. The pain also bothers during urination and bowel movements.
Together with the listed first symptoms of prostatitis, fever, fever are possible. Urinary retention may occur gradually. This is due to the development of edema of the prostate gland, as a result of which its tissue compresses the urethra.
How are the symptoms of prostatitis in men in chronic form? First of all, you should pay attention to such signs of prostatitis:
problems with erection, potency;
rapid onset of ejaculation;
difficulties with urine excretion (the jet is interrupted, you have to squeeze, there is a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder and others);
there are discharge from the urethra;
depressed mood, breakdown, rapid onset of fatigue.

It is important that in the chronic course of prostatitis in men, its symptoms may be completely absent or appear only during periods of exacerbation. So, with a relapse of the pathology, there are possible signs of prostate disease, such as pain in the sacral spine, pressing sensations in the region of the anus, rectum. Such manifestations (in the absence of other symptoms of inflammation of the prostate gland) can lead to the thought of the development of diseases of the sacrum or intestines, therefore, thorough diagnosis is required before treatment.
Ignoring signs of prostatitis, postponing a visit to the doctor “for later” can lead to complications in men, including:
infertility;
constant exhausting pain in the perineum;
depressive disorders, neurosis;
impotence.
Clinical examination